In today’s rapidly evolving IoT landscape, choosing the right connectivity solution is critical to the success of any IoT project. Whether you’re deploying smart meters, tracking assets, or managing a fleet of connected devices, the network technology you choose can significantly impact performance, cost, and scalability.
Among the most prominent IoT connectivity solutions are NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT), LTE-M (Long Term Evolution for Machines), and Sigfox. Each offers unique advantages and trade-offs, catering to different use cases and requirements.
In this article, we’ll take a detailed look at NB-IoT, LTE-M, and Sigfox. By comparing their features, benefits, and ideal use cases, we’ll help you determine which technology best suits your IoT application. Whether you’re optimizing for coverage, power efficiency, or data throughput, this guide has you covered.
Let’s dive in!
What are NB-IoT, LTE-M, and Sigfox?
What is NB-IoT?
NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT) is a Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technology standardized by 3GPP. It operates on licensed cellular spectrum and is optimized for applications that require:
- Deep indoor coverage
- Low data rates
- Minimal power consumption
NB-IoT is ideal for stationary IoT devices, such as smart meters or environmental sensors, which transmit small amounts of data intermittently. Due to its power-saving features (like PSM and eDRX), devices running on NB-IoT can last for years on a single battery.

Key Features of NB-IoT:
- Licensed cellular spectrum (reliable and interference-free)
- Ultra-low power consumption
- Excellent deep indoor and underground coverage
- Suited for applications with limited mobility
What is LTE-M?
LTE-M (Long Term Evolution for Machines) is another LPWAN technology developed by 3GPP, designed to work over existing LTE networks. It offers higher data rates and lower latency than NB-IoT, making it ideal for applications requiring:
- Real-time data transmission
- Mobility (e.g., asset tracking)
- Two-way communication
LTE-M supports mobile IoT use cases, like wearable devices, logistics tracking, and smart vehicles, thanks to its seamless handover between cell towers. While it consumes slightly more power than NB-IoT, LTE-M strikes a balance between performance and efficiency.
Key Features of LTE-M:
- Licensed cellular spectrum for high reliability
- Higher data rates and lower latency compared to NB-IoT
- Supports mobility and real-time communication
- Ideal for IoT applications requiring voice or frequent data exchange
What is Sigfox?
Sigfox is a proprietary LPWAN technology that operates on unlicensed spectrum (ISM bands). Unlike NB-IoT and LTE-M, Sigfox is designed for ultra-low bandwidth applications that only need to send small, infrequent messages. This makes Sigfox a cost-effective choice for simple, battery-efficient IoT devices.
However, Sigfox’s limitations include lower data rates, higher latency, and restricted downlink capabilities. It’s ideal for low-complexity use cases such as basic sensor monitoring and asset tracking where minimal data transmission is sufficient.
Key Features of Sigfox:
- Operates on unlicensed spectrum (low-cost connectivity)
- Extremely low power consumption
- Limited data capacity (small message size)
- High latency and restricted bidirectional communication
By understanding the fundamentals of NB-IoT, LTE-M, and Sigfox, you can better appreciate their unique strengths and applications. In the next section, we’ll compare their features side by side to highlight their differences.
Comparison Table
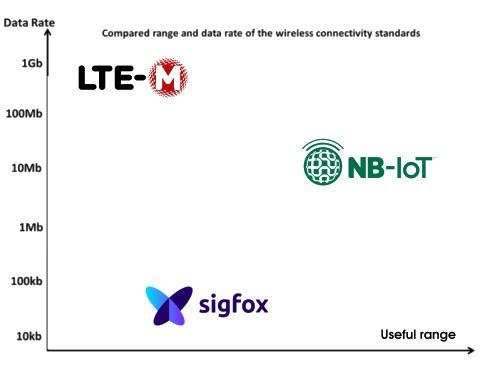
For quick reference, here’s a side-by-side comparison of NB-IoT, LTE-M, and Sigfox:
| Feature | NB-IoT | LTE-M | Sigfox |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Type | Licensed cellular | Licensed cellular | Unlicensed ISM spectrum |
| Data Rate | Up to 250 kbps | Up to 1 Mbps | ~100 bps |
| Power Efficiency | Very high | High | Very high |
| Coverage | Deep indoor/underground | Strong (indoor/outdoor) | Moderate |
| Latency | Higher | Low | High |
| Mobility Support | Low | High | Limited |
| Security | Strong (3GPP standards) | Strong (3GPP standards) | Basic |
Key Takeaways
- NB-IoT is best for stationary devices requiring deep coverage and long battery life.
- LTE-M excels in applications that need mobility, higher data rates, and real-time performance.
- Sigfox is ideal for low-cost, low-complexity use cases with minimal data transmission.
In the next chapter, we’ll explore the ideal use cases for each technology to help you determine which one aligns best with your IoT needs.
NB-IoT vs LTE-M vs Sigfox: Benefits and Drawbacks
Each IoT connectivity technology—NB-IoT, LTE-M, and Sigfox—has its strengths and limitations. The right choice depends on your use case, data requirements, and deployment environment. In this section, we’ll explore the key benefits and drawbacks of each technology.
NB-IoT: Benefits and Drawbacks
Key Benefits:
- Deep Indoor Coverage: NB-IoT excels in penetrating walls, basements, and underground areas, making it ideal for devices in challenging environments like smart meters or water sensors.
- Ultra-Low Power Consumption: With power-saving features like PSM and eDRX, NB-IoT devices can operate for up to 10 years on a single battery.
- Low Deployment Cost: Leveraging existing cellular infrastructure lowers deployment costs while providing reliable connectivity.
- Licensed Spectrum: Ensures secure and interference-free communication.
Drawbacks:
- Limited Mobility: NB-IoT is not designed for devices that move frequently, as it does not support cell tower handovers effectively.
- Low Data Rates: While sufficient for most sensor-based applications, the data rate (up to 250 kbps) limits NB-IoT’s use for more advanced or real-time applications.
- Higher Latency: The technology supports higher latency, which may not be suitable for time-sensitive applications.
LTE-M: Benefits and Drawbacks
Key Benefits:
- Supports Mobility: LTE-M offers seamless handovers between cell towers, making it ideal for mobile IoT applications such as fleet management and asset tracking.
- Low Latency: Provides near real-time data transmission, enabling applications that require immediate communication.
- Higher Data Rates: With speeds up to 1 Mbps, LTE-M supports more advanced applications, including voice and firmware updates.
- Reliable and Secure: Operates on licensed spectrum with cellular-grade security, ensuring robust and secure communication.
Drawbacks:
- Higher Power Consumption: While efficient, LTE-M consumes more power than NB-IoT, making it less ideal for ultra-long battery life use cases.
- Slightly Higher Cost: LTE-M’s advanced features come at a slightly higher cost compared to NB-IoT and Sigfox.
- Moderate Indoor Penetration: While LTE-M performs well indoors, it’s not as effective as NB-IoT for deep indoor coverage.
Sigfox: Benefits and Drawbacks
Key Benefits:
- Low Cost: Sigfox offers one of the most affordable IoT connectivity options, with minimal operational costs.
- Ultra-Low Power Consumption: Sigfox is extremely power-efficient, making it ideal for devices that need to send small amounts of data over long periods.
- Simplicity: Its straightforward network design and low data capacity requirements simplify device implementation and maintenance.
Drawbacks:
- Limited Data Capacity: Sigfox is restricted to very small message sizes (12 bytes per uplink), which limits its use to simple, low-bandwidth applications.
- High Latency: Sigfox’s transmission delays make it unsuitable for time-sensitive applications.
- Limited Downlink Capability: While uplink (device to cloud) works well, downlink (cloud to device) communication is highly restricted.
- Network Reliability: Operating on unlicensed spectrum increases the risk of interference and reduces reliability compared to licensed options like NB-IoT and LTE-M.
Summary of Benefits and Drawbacks
Here’s a quick overview of the benefits and limitations of each technology:
| Technology | Key Benefits | Key Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| NB-IoT | – Deep indoor coverage – Ultra-low power consumption – Low cost – Licensed spectrum | – Limited mobility – Low data rates – Higher latency |
| LTE-M | – Supports mobility – Low latency – Higher data rates – Licensed spectrum and security | – Higher power consumption – Slightly higher cost – Moderate indoor penetration |
| Sigfox | – Low cost – Ultra-low power – Simple and reliable for basic tasks | – Limited data capacity – High latency – Limited downlink and reliability |
Key Takeaways
- Choose NB-IoT for applications requiring deep coverage, low power consumption, and stationary deployments.
- Choose LTE-M when mobility, low latency, and higher data rates are essential, such as in asset tracking or wearable devices.
- Choose Sigfox for ultra-simple, low-cost use cases with minimal data transmission needs, like basic sensors.
In the next chapter, we’ll explore the ideal use cases for each technology to provide a clearer picture of where they excel.
Which IoT Connectivity Solution Should You Choose?
Choosing between NB-IoT, LTE-M, and Sigfox depends on the specific requirements of your IoT project. To make the decision easier, let’s summarize the key factors to consider, including data requirements, mobility, power consumption, and cost.
Decision Factors to Consider
- Data Requirements
- If your application requires frequent, larger data transfers (e.g., real-time monitoring), LTE-M is the best choice due to its higher data rates.
- For low-volume, periodic data transfers, such as sensor updates, NB-IoT and Sigfox are better options.
- Mobility
- For applications involving moving devices (e.g., fleet tracking, wearable devices), LTE-M is the clear winner due to its seamless handover between cell towers.
- If the device is stationary (e.g., smart meters or fixed sensors), NB-IoT or Sigfox will perform efficiently.
- Power Consumption
- For ultra-low power applications requiring years of battery life, both NB-IoT and Sigfox excel.
- LTE-M consumes slightly more power but strikes a balance between power efficiency and performance.
- Coverage
- For devices in deep indoor or underground locations, such as basements or tunnels, NB-IoT offers superior coverage.
- LTE-M provides strong indoor and outdoor coverage, but it’s slightly less effective in penetrating walls than NB-IoT.
- Sigfox performs well in open environments but struggles with deep indoor penetration.
- Latency
- If your application requires real-time communication (e.g., health monitoring or vehicle connectivity), LTE-M is the best option due to its low latency.
- NB-IoT and Sigfox are suitable for applications where higher latency is acceptable.
- Cost
- For cost-sensitive deployments, especially in large-scale projects, Sigfox offers the most affordable solution.
- NB-IoT is moderately priced, balancing performance and cost-effectiveness.
- LTE-M is slightly more expensive due to its advanced features but offers better performance for more complex use cases.
Quick Decision Guide
Use the table below to determine the best IoT connectivity technology for your needs:
| Requirement | NB-IoT | LTE-M | Sigfox |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Volume | Low | Medium | Very Low |
| Mobility | Low | High | Limited |
| Power Consumption | Ultra-Low | Low | Ultra-Low |
| Latency | Moderate | Low | High |
| Coverage (Indoor/Underground) | Excellent | Good | Moderate |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate-High | Low |
| Best Use Cases | Smart meters, environmental sensors | Asset tracking, wearables, healthcare | Basic sensors, parking, waste management |
Making the Final Decision
- Choose NB-IoT if:
- You need deep indoor coverage or deployment in remote areas.
- The device is stationary and transmits small amounts of data.
- Ultra-long battery life is a top priority.
- Choose LTE-M if:
- Your devices require mobility or frequent data transmission.
- Real-time communication and low latency are essential.
- You need higher data rates for complex applications.
- Choose Sigfox if:
- Your project requires a low-cost, ultra-low power solution.
- Data transmission is infrequent and limited to small payloads.
- You’re deploying simple, static sensors in open environments.
Real-World Example Scenarios
- Utility Smart Metering
- Solution: NB-IoT
- Why: Stationary devices, deep indoor deployment, and low data requirements.
- Fleet Tracking for Logistics
- Solution: LTE-M
- Why: Mobility, seamless handovers, and real-time location updates.
- Smart Bins for Waste Management
- Solution: Sigfox
- Why: Simple, low-cost sensors with minimal data needs.
- Wearable Health Monitoring Devices
- Solution: LTE-M
- Why: Low latency, high data rates, and mobility support.
- Air Quality Sensors in Smart Cities
- Solution: NB-IoT
- Why: Stationary deployment, low power consumption, and reliable connectivity.
Conclusion: Choosing NB-IoT, LTE-M, or Sigfox
The choice between NB-IoT, LTE-M, and Sigfox depends on your project’s needs:
- NB-IoT: Best for stationary devices requiring deep indoor coverage, long battery life, and low data rates.
- LTE-M: Ideal for mobile applications, real-time communication, and higher data throughput.
- Sigfox: Suited for simple, cost-effective solutions with minimal data transmission.
For businesses that need flexibility, Waltero’s W-Sensor offers a powerful advantage by supporting both NB-IoT and LTE-M. This allows the sensor to dynamically optimize connectivity based on local conditions, ensuring reliable performance and power efficiency regardless of deployment environment.

