Germany is well developed in terms of both NB-IoT and LTE-M, with infrastructure present nationwide and a wide range of local and roaming service providers offering both technologies. The German IoT sector has rapidly grown its presence with a 137% increase between 2018 and 2023. Furthermore, the smart service and maintenance technology has a 50% adoption rate, compared to a 28% global adoption rate.
Waltero collaborates with leading telecom providers through both direct partnerships and roaming agreements to ensure reliable IoT network coverage. Additionally, some customers opt to source their own connectivity solutions.
Leading Network Providers in Germany:
- Deutsche Telekom: Offers nationwide LTE-M and NB-IoT coverage, supporting a wide range of IoT applications. Had completed the rollout of LTE-M and NB-IoT by 2020.
- Vodafone: Provides extensive NB-IoT coverage across Germany, facilitating connectivity in both urban and rural areas.
Narrowband - Telefónica (O2): Focuses on LTE-M deployments, enhancing IoT connectivity for industrial applications.
Onomondo
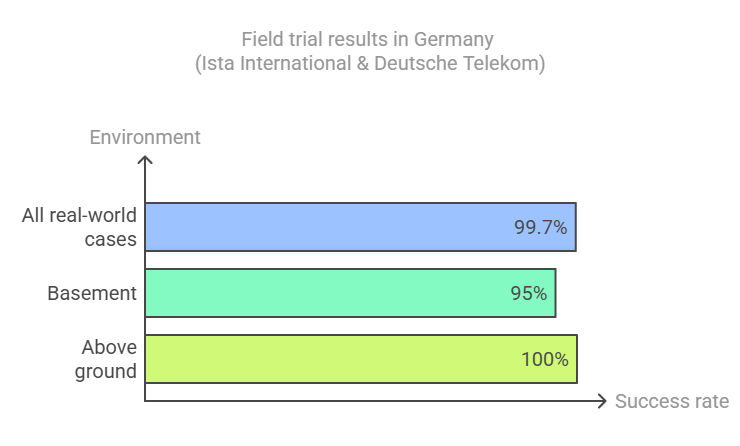
Field trials conducted by Ista International GmbH and Deutsche Telekom demonstrated that NB-IoT could establish stable connections and transmit data in 99.7% of real-world cases, including 100% success in above-ground scenarios and 95% in basements.
Network Providers in Germany that do not publicly offer NB-IoT or LTE-M:
The network providers below do not publicly offer NB-IoT or LTE-M as of now.
- NetCologne
- Deutsche Breitband Dienste
Roaming providers that offer NB-IoT and LTE-M in Germany:
In addition to the local providers listed above, there are a number of roaming providers that also offer IoT coverage in Germany, utilizing the local network infrastructure. Using a roaming provider can even be beneficial, as they can then choose between different networks, depending on what coverage is strongest in any given location. The drawback is that in some cases, they will get a lower priority within a network than the network owner’s own connectivity solution.
There are many companies that offer access to IoT networks through roaming, including both large players such as Elisa, Orange, BT Group and Tele2, in addition to roaming specialists such as Onomondo and 1nce.
NB-IoT and LTE-M:
NB-IoT (Narrowband Internet of Things)
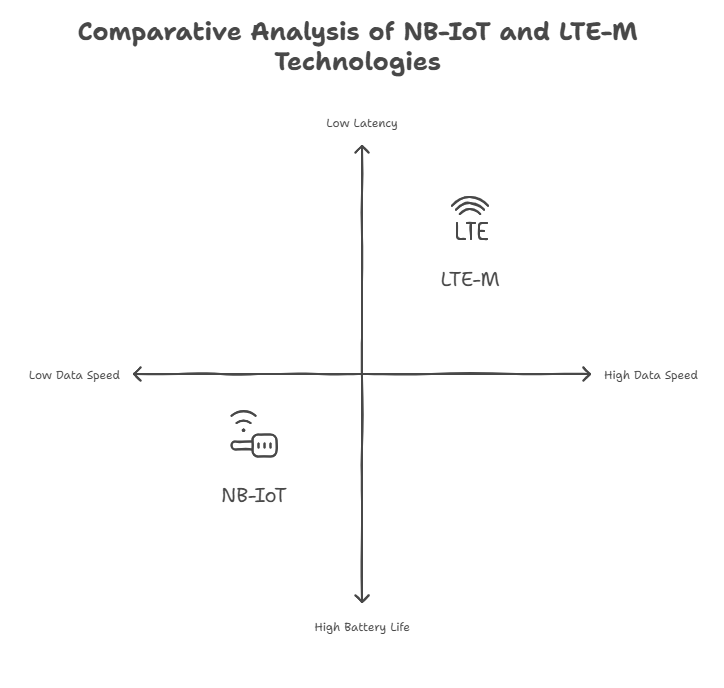
NB-IoT is a low-power, wide-area wireless technology designed for IoT applications that require low data rates and excellent coverage. It provides long battery life, deep indoor penetration, and supports a high density of devices, making it ideal for large-scale deployments like smart metering and environmental monitoring.
Deutsche Telekom and Vodafone have achieved nationwide NB-IoT coverage, ensuring reliable connectivity across urban and rural areas. Narrowband
NB-IoT’s power efficiency enables devices to operate for extended periods on a single battery, reducing maintenance costs for utilities.
LTE-M (Long-Term Evolution for Machines)
LTE-M is a low-power, wide-area wireless technology designed for IoT applications that require moderate data speeds and mobility. It operates on existing 4G LTE networks, offering extended battery life, low latency, and reliable coverage for devices in both stationary and mobile scenarios.
Takeaways:
In summary, NB-IoT and LTE-M are already well-established in Germany with infrastructure set in place nationwide. Both of these technologies being present means that IoT installations can choose between the two to optimize for local conditions. NB-IoT provides better connectivity through deep indoor penetration, and endures higher latency, whereas, LTE-M offers the possibility of transferring more data, at the expense of needing lower latency. Some IoT devices, such as Waltero’s W-sensor, are able to choose between transmitting on either network. This means that you can get the best out of the device for any specific location, both in terms of efficient power consumption and speed and accuracy of the data transmissions.
